The cycle of annual plants
Posted By VOTRE ALARME AVEC TLSURVEILLANCE Tina Touzi on 06-11-2023 11:11:43
Description
1. The cycle of annual plants
An annual plant is characterized by a life cycle of one year.
– At the beginning of spring, when climatic conditions become favorable for seed germination, they form a small root and a young stem which become a seedling.
For seeds to germinate, sufficient humidity and a mild temperature are required. These conditions are met in spring when there is abundant rain and the days are warmer.
– At the end of spring, if conditions remain favorable, this seedling grows sufficiently to become an adult plant.
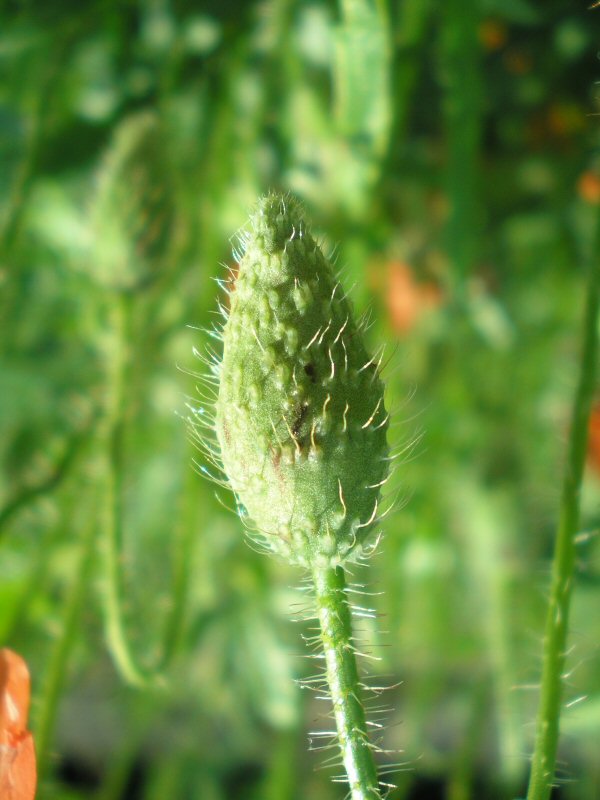
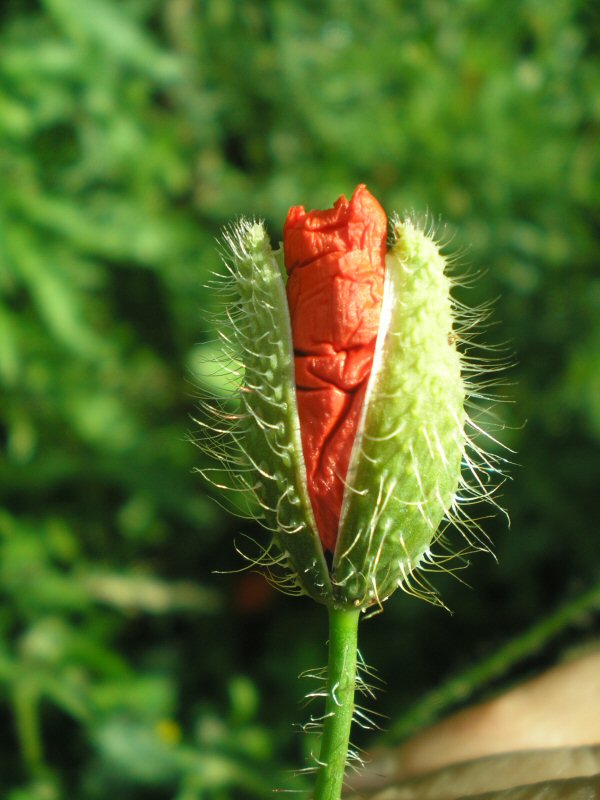
This plant produces flower buds that open and produce flowers. Flowers are the organs necessary for plant reproduction.
They have different organs such as the pistil and stamens.
– When pollen from flowers is carried on the pistil of the same flower or other flowers, these flowers produce seeds which are protected by a fruit.
– During the summer, the fruit develops and takes different shapes.
– In the fall, the entire plant withers and dies, the fruits fall, rot and thus release the seeds which are buried in the ground.
– During the winter, these seeds, very resistant to the cold, will remain in the ground until the following season. They can even remain in the ground for several years without germinating if the germination conditions are not met, because they are also very resistant to drought.
2. The cycle of perennial plants
Perennial plants do not die completely in winter. Part of the plant disappears, but some of their organs survive during the winter and develop again the following spring.
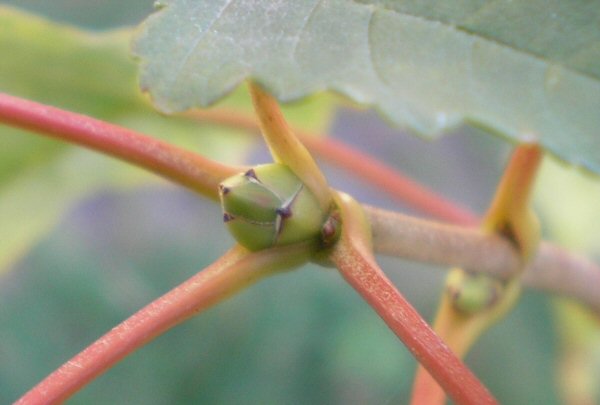
In autumn, the deciduous leaves of shrubs (example: vine) and trees (examples: chestnut tree, plane tree) fall. The aerial buds become very visible, but their scales protect them well from the cold and rain. Certain herbaceous plants (example: tulip, daffodil, iris, Solomon's seal) lose both their stems and their leaves, and only retain their underground buds.
In winter, these organs of resistance to cold and drought appear in several forms such as roots, tubers, rhizomes and bulbs, which are underground organs (they become invisible above the ground) as well as the trunks and branches, which are the aerial organs (they remain visible above the ground).
Perennial plants live for several years. All resistance organs contain nutrient reserves and buds, tiny leafy branches enclosed in scales which protect them against rain, drying out and shock.
In spring, the aerial and underground buds hatch when climatic conditions become favorable again and the sap circulates again. They generate new branches and new stems, carrying leaves, flowers or new buds.
The essential
Plants occupy the environments in a varied manner throughout the seasons.
In winter, annual plants disappear. Only their seeds survive in the soil while waiting for good germination conditions.
Perennial plants have organs that survive all winter. Some have small or glazed evergreen leaves that remain over winter. Others have deciduous leaves that fall from the branches, leaving only the buds visible during the winter. Still others have buds on their underground cold-resistant organs.
Buds and seeds develop when climatic conditions are favorable.
Related Blogs
Food, preventive against cancer
Stress, how to deal with it?
The Role of Content in SEO Marketing Content
The Comprehensive Guide to Off-Page SEO
Keyword Research SEO marketing
Ratings & Review
Popular Blogs
Free for dev - list of software-2 (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, etc.)
Developers and Open Source authors now have a massive amount of services offering free tiers, but it can be hard to find them all to make informed decisions. This is a list of software (SaaS,...
Free for dev - list of software-3 (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, etc.) (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, etc.)
Developers and Open Source authors now have a massive amount of services offering free tiers, but it can be hard to find them all to make informed decisions. This is a list of software (SaaS,...
Climate Change Amnesty International
It’s easy to take our planet for granted until we see the human cost of its degradation: hunger, displacement, unemployment, illness and deaths. Millions of people are already suffering from the...
Recently Added Blogs
Name, Address, and Phone (NAP) information across online directories
In the digital age, a business's online presence plays a crucial role in attracting customers and establishing credibility. One essential aspect of this online presence is the Name, Address, and...
Name, Address, and Phone (NAP) information across online directories
In the digital age, a business's online presence plays a crucial role in attracting customers and establishing credibility. One essential aspect of this online presence is the Name, Address, and...
The Origins of the Universe: Understanding the Big Bang Theory
The Big Bang Theory stands as one of the most widely accepted explanations for the origins of the universe. This theory proposes that the universe began as an infinitely small, dense point and has...
Login to your Be found account
Sign in by Email
No Account yet? Click here to signup
Already have an account? Sign In
FEEDBACK / SUGGESTIONS
Give us your valuable feedback to make website more user friendly

Leave your details below